[ad_1]
The good news about hypertrophy is that it’s kind of simple for a lot of athletes: train hard, eat in a slight caloric surplus, and get enough sleep. Here’s the bad news about building muscle: it doesn’t happen overnight.
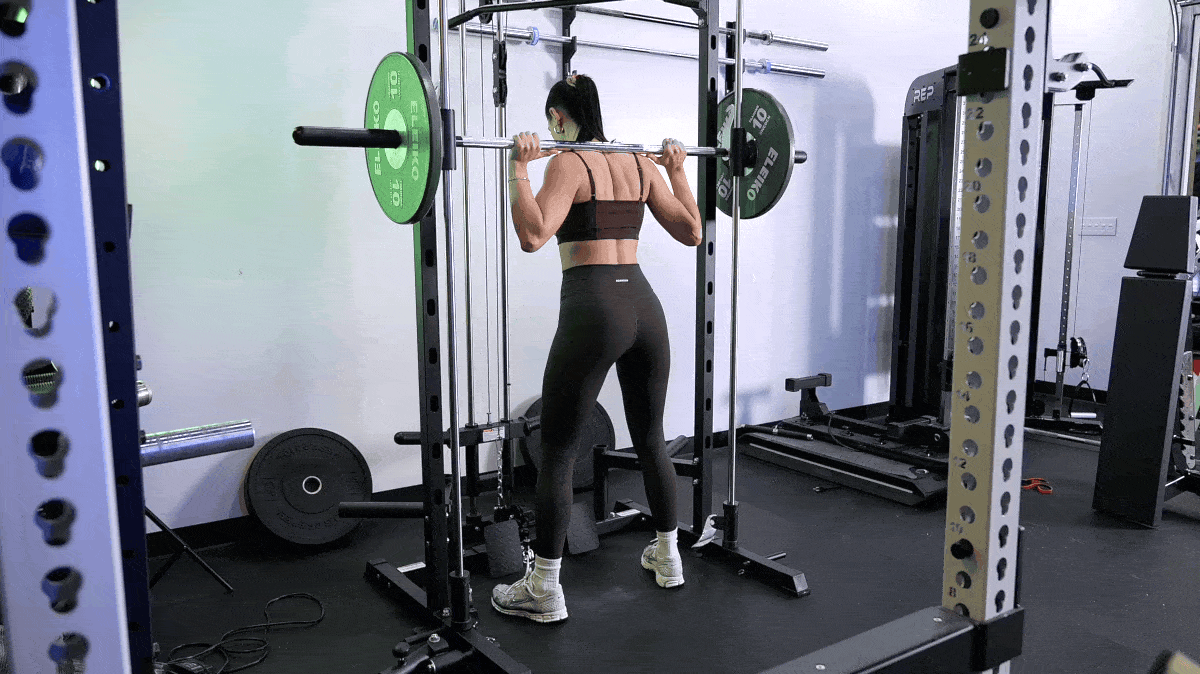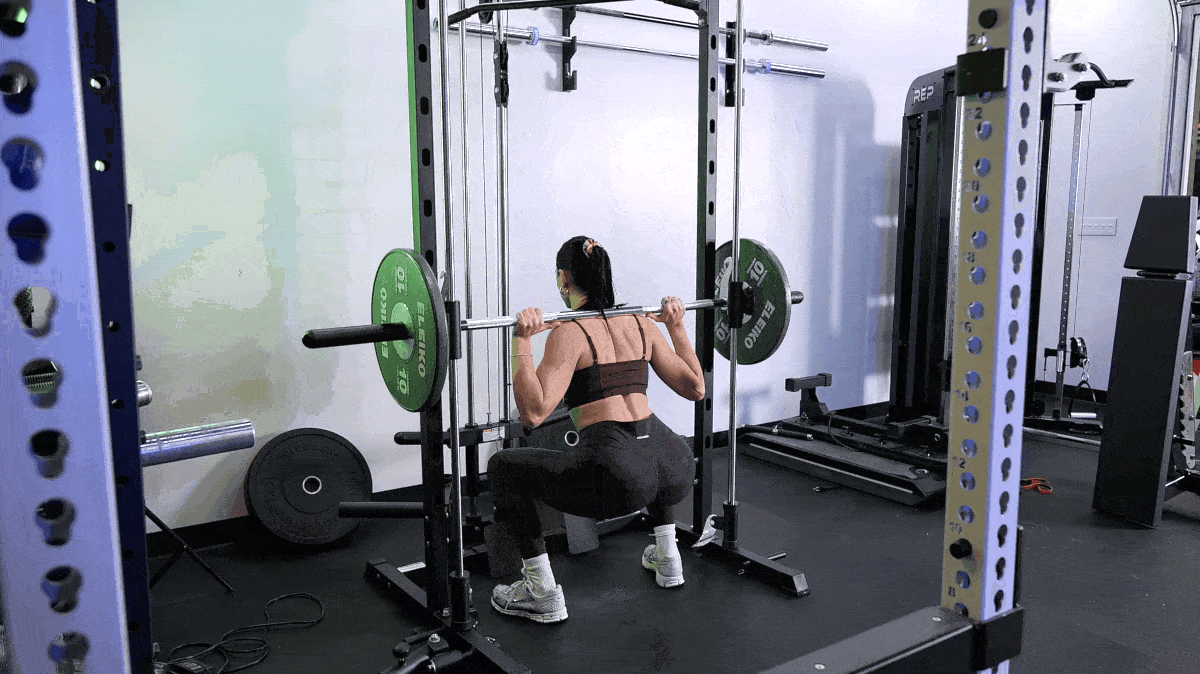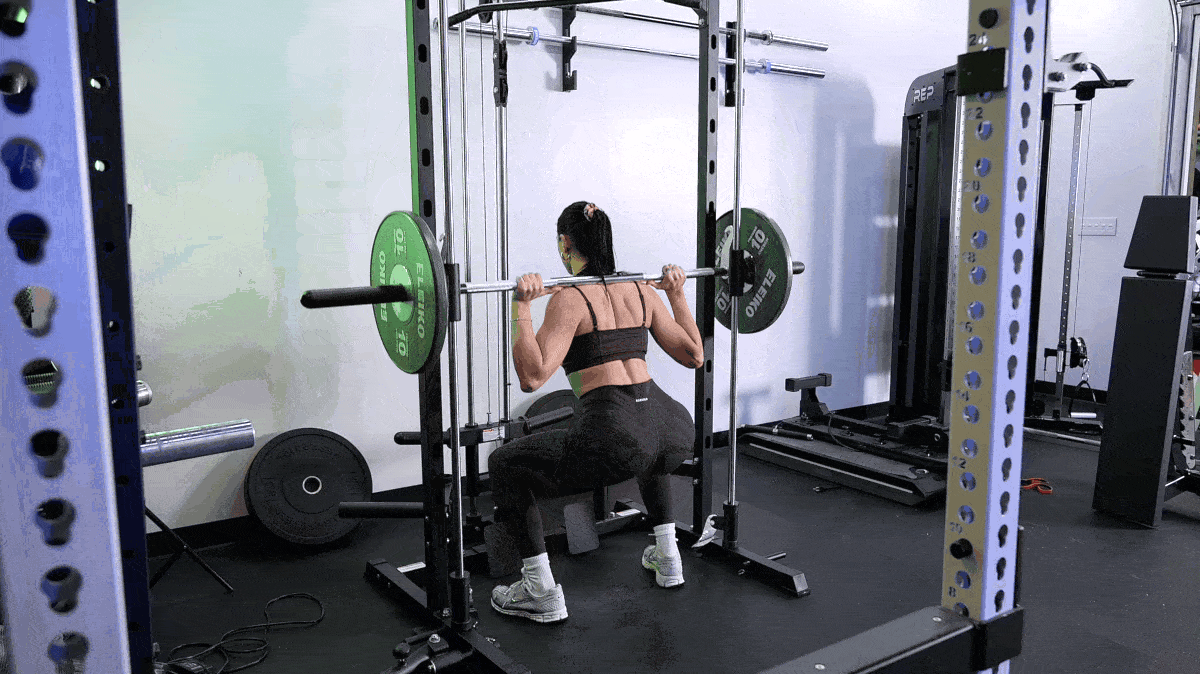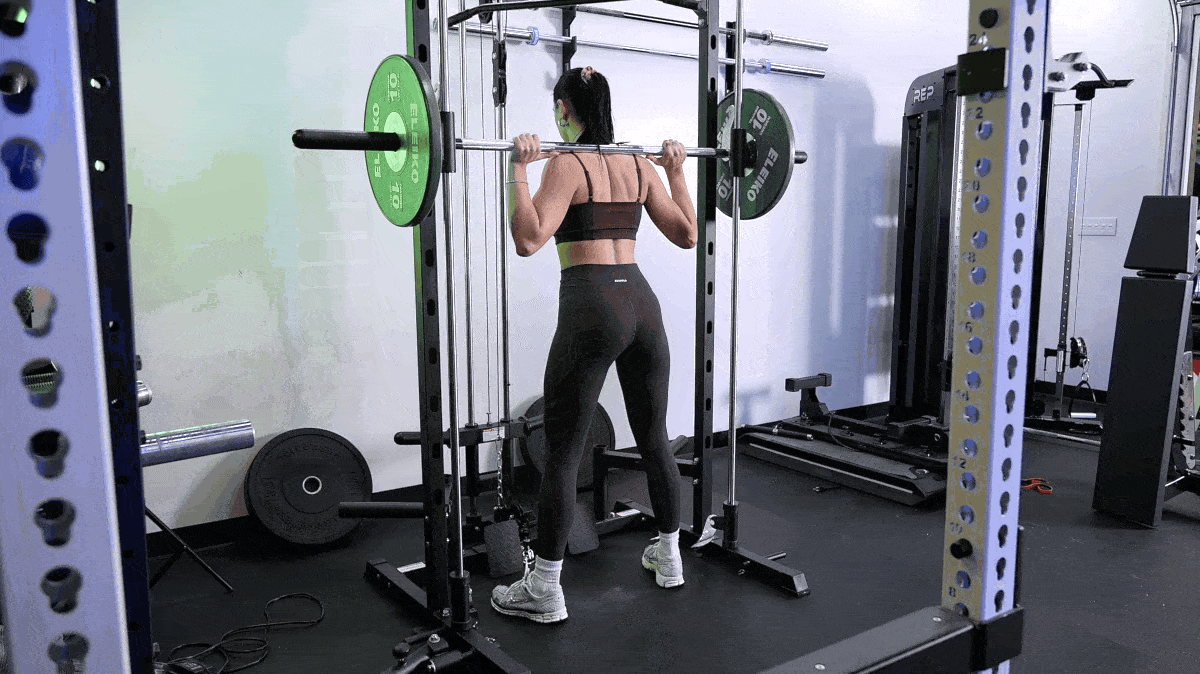
But that doesn’t mean there’s nothing you can do to speed up muscle growth. Here are our top tips to build muscle fast, including the best exercises to do and foods to eat.
Key Takeaways
- The process of muscle growth, known as muscle hypertrophy, typically takes 10-12 weeks, but can be made faster with the proper exercises, rest, and protein intake. (1)
- To optimize muscle growth, try consuming at least 0.7 grams of protein per pound of body weight per meal. You can reach this by eating high-protein foods like salmon, eggs, Greek yogurt, and chicken.
- Get plenty of sleep. Human growth hormone (HGH), which promotes muscle growth and repair, is produced in the body while sleeping.
- Compound exercises like the back squat, bench press, deadlift, and overhead press are good for muscle building.
8 Science-Backed Tips to Build Muscle Fast
When hypertrophy is the goal, you need a solid weight training program that hits all of your major muscle groups, includes rest days, and features a meal plan with plenty of calories, protein, and carbohydrates. Sounds simple enough. But if you want to see more muscle mass sooner, here is how to tweak each of these areas to your benefit.
1. Do Eccentric Training
When you set out to lift weights, you know that you’re basically going to pick something up, and then put it back down. The fancy way to refer to these parts of the lift are the eccentric and concentric phases.
The eccentric phase is when the muscles lengthen, typically the lowering down part of an exercise. Think: lowering into a squat, hinging to the bottom of a deadlift, or lowering down from a pull-up or into a push-up.
Technically speaking, your muscles are forced to contract while stretched due to an external load’s force. When comparing concentric and eccentric training, research suggests eccentric training is slightly more effective at stimulating hypertrophy. (1)(2)
There are a few potential reasons why. Eccentric training is a way of increasing intensity without necessarily lifting heavier weights. Your muscles spend more time under tension, especially if you move slower, which adds more stress to your muscle fibers. (That stress is great for building muscle mass.)
Research also suggests that focusing on the eccentric portion increases muscle protein synthesis and releases more IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1, a growth hormone). (3)
[Read More: The Ultimate Workout Split, Created by Our Experts]
You can do eccentric-only exercises, which are a bit more limited, or various exercises using slow-tempo training. In tempo training, slowing down the eccentric phase lets you do fewer reps but increases time under tension, which is associated with potentially faster hypertrophy. Irradiating tension while focusing on proper form also helps. (1)
Research suggests a general tempo recommendation for hypertrophy training: two to four seconds for the eccentric phase and one to three seconds for the concentric phase. But you can play with that even further for an eccentric focus. (3)
Eccentric-Only Exercises
- Eccentric Pull-Up
- Eccentric Push-Up
- Eccentric Lunge
Focus on the Eccentric Phase with Tempo Training
2. Emphasize Compound Movements for Major Muscle Groups
Some research suggests that one effective hypertrophy program that maximizes muscle growth follows the following formula: three to six sets of six to 12 reps with 60-second rest breaks at a moderate intensity (60 to 80 percent of your one-rep max or 1RM). Aim for 12 to 20 sets per muscle group per week. (1)(5)
Which exercises should you choose to reach those numbers? Both multi-joint and single-joint exercises are important, so don’t throw out your biceps curls yet; just save them for later in your session.
Still, you’ll likely want to emphasize compound, multi-joint exercises. Compound movements help with hypertrophy because they recruit more of muscle mass to get the job done. Research shows greater anabolic hormonal response after training multi-joint exercises, and higher levels of testosterone and growth hormone get released than when using single-joint exercises. (3)

[Read More: Powerbuilding Workout Routine, With Tips from a CPT]
Additionally, compound movements require other muscles in your body to contract and stabilize, even if they are not the ones working. Though a squat may not seem like an ab workout, over 200 smaller muscles work to stabilize your core and spine while you move your hips and legs. (3)
Single-joint exercises still have their place because they allow you to focus more on individual muscles, particularly smaller, neglected muscles. These may even out imbalances in size, appearance, and function. (3)
Best Compound Exercises in Strength Training
3. Do Higher Training Volume
There is some controversy around training volume and hypertrophy. Is more always better?
Training volume refers to the total product after multiplying sets times reps times load in a training session. A lot of research associates higher volume with higher hypertrophy. It may be because there is more muscular tension, damage, or metabolic activity. More metabolic activity may also release more growth hormones. (3)
Other research also finds a positive relationship between higher training volume and more hypertrophy, especially in already trained lifters for whom it becomes more difficult to continue gaining muscle fast. (6)(7)
The trouble is that aiming for a super high volume can make training sessions too long. Some research shows that training for more than one hour decreases the quality of work. You may not be able to exert the same level of effort, and your good form could suffer. That’s why playing with tempo and focusing on major muscle groups can help maximize your hour (or so). (3)
[Read More: How to Do 100 Push-ups a Day, Advice and Programming from a CPT]
Other studies find that a lower load (30 to 60 percent of your 1RM) yields similar hypertrophy to a higher load (greater than 60 percent of your 1RM) if you can reach failure in the lower load. But, it also adds that you don’t have to go to failure for hypertrophy. (1)
Ways to Play With Volume
- Vary your load: lift a little lighter for more reps or heavier for fewer reps.
- Vary your sets: do supersets with agonist and antagonist muscles, upper and lower body supersets, drop sets, and cluster sets. (1)
- Mix volume with intensity — if you’re on a strict program to increase volume, play with adding one day where you go for high intensity at a lower volume.
4. Use Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is key to making gains. Of course, it takes time, so it might not be your first thought when trying to build muscle fast. Still, it can help over two to three months.
When you start a resistance training program, the gains you see in the first four weeks may mainly be due to muscle damage and muscle cell swelling. Real muscle growth may occur after six to 10 weeks—so you can use progressive overload to your advantage in this time frame. And if you’re a seasoned lifter struggling to gain muscle, use it to help bust through a physique plateau. (1)
Progressive overload refers to changing one variable at a time throughout a training program to continue adding new stress to your muscles. But progress isn’t always linear, and lifting heavy weights isn’t necessarily your intention for hypertrophy, so you need to do more than just increase the weight.
Here are some examples of variables.
Training Variables
- Volume (sets and reps)
- Load
- Intensity
- Rest Periods
- Exercise Angle
- Range of Motion
- Unilateral Training
- Tempo Training
- DUP Training (Daily Undulating Periodization)
5. Eat Enough Calories
You know what to do in the gym — now you need to tackle your meal plan. When you train, muscle protein breakdown occurs. When you eat enough of the right stuff, muscle protein synthesis occurs. When muscle protein synthesis exceeds muscle protein breakdown, hypertrophy happens. (1)
You need to be in an energy surplus, meaning you take in more calories than you burn. (8)
Exactly how many calories you need depends on multiple factors. Start with BarBend’s calorie calculator.
What kind of calories you eat will also influence your body composition. Next, use BarBend’s macros calculator to help figure out the right balance of protein, carbs, and fat your body needs.
Once you have that, you need one more calculator to refine things even more — the protein intake calculator.
Protein Intake Calculator
What to Do With Your Number Goals
- Tracking your calories and macros can ensure you hit your goals.
- For people with a history of disordered eating who don’t want to count and track, you may want to look into eating intuitively as a bodybuilder.
6. Try Protein Powder
After calculating your protein intake needs to build muscle fast, you likely found a high number. You can reach your goal by packing your diet with high-protein foods. If you struggle to hit it every day, adding protein powder to a shake can help you achieve your daily goal quickly and easily.
Protein Powder Tips
- Whey Protein is your best bet if you consume dairy. It’s a high-quality, complete protein source that contains all the amino acids your body needs to build muscle after training. It is highly bioavailable and can be rapidly absorbed, potentially leading to faster muscle protein synthesis. (9)
- Soy Protein is also a high-quality, complete protein source and a great alternative protein powder for vegan athletes.
- Getting 20 to 40 grams of protein (one or two scoops) within three hours of your workout may help stimulate muscle protein synthesis. (10)
- Adding a source of carbs to your protein shake can also help with muscle recovery. (10)
- Having a protein shake before bed may also increase overnight muscle protein synthesis.
7. Try Creatine
Creatine is one of the most well-researched sports supplements. Fifty years of research and hundreds of studies show that it is a safe ergogenic aid for exercise performance. It increases your stored energy and exercise capacity to withstand a higher volume. Over time, it can help you build muscle when combined with a resistance training program. (11)
Creatine Tips:
- Creatine Monohydrate is the best form of creatine to choose from; all of the research is on this type.
- The International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) suggests the following protocol for taking creatine since it is no longer believed that you need a creatine loading phase. (11)
- Take 0.3 grams of creatine monohydrate per kilogram of body weight per day for five to seven days.
- Take three to five grams of creatine daily. This dosage should increase your creatine stores in three to four weeks and potentially help you build muscle faster.
8. Take Rest Days and Get Enough Sleep
You’ve trained hard and eaten well. The final step is…to go to sleep. The last piece of the puzzle to faster muscle growth is rest, muscle recovery, and, yes, getting to bed earlier.
Muscle protein synthesis begins about four hours after resistance training and may double 24 hours later. So, your muscles are still growing up to a day after your session. Many athletes train two days in a row, but allowing one or two rest days gives your body a chance to recover, repair damaged tissues, and stimulate growth. Rest is also when your body secretes growth hormone and anabolic activity occurs. (12)(13)
You also grow while you sleep. Sleep is important for immune function, growth hormone secretion, and muscle protein synthesis. (14) So, it’s especially important to sleep well (and a lot) between training sessions.
Work Rest Into Your Workout Routine:
- Take at least one full rest day per week, with an optional second day of active recovery where you can do light cardio or mobility work.
- Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night.
Best Exercises to Build Muscle Fast
Ready to grow? Here are the best exercises for each of your major muscle groups.
Exercises for Big Chest Muscles
To build a big chest, you’ll need a mix of big compound movements followed by isolation lifts. Here are the best chest exercises you’ll want to choose on your journey for gains.
Exercises for Big Back Muscles
To build a bigger back, you want to focus on compound pulling movements in all directions, target your lats, and isolate the smaller back muscles. These are the best back exercises to hit all areas.
Exercises for Big Shoulder Muscles
Strong shoulders fill out your T-shirts and help improve performance in many lifts. You’ll want a good mix of compound movements, isolation exercises, and unilateral work. Here are the best shoulder exercises for a well-rounded look.
Exercises for Big Arm Muscles
Building bigger arms means focusing on three major areas: triceps, biceps, and forearms. The best arm exercises incorporate all three. Be sure to mix in bilateral and unilateral work.
Best Triceps Exercises:
Best Biceps Exercises:
Best Forearm Exercises:
Core
Build all of your ab muscles in the best core exercises. They’ll target your rectus abdominis (six-pack), transverse abdominis, and obliques (side abs) for 360 degrees of sculpted work.
Glutes
For bigger glutes, you’ll want to hit your main lower body compound lifts, and some extras. Here are the best glute exercises.
Legs
It’s leg day, and well-rounded legs mean solid quads, hamstrings, and calves. Of course, you’ll work them in the glute exercises, but these are a little more targeted. Include bilateral and unilateral work in these best leg exercises.
Best Quad Exercises:
Best Hamstring Exercises:
Best Calf Exercises:
Best Foods to Build Muscle Fast
Choosing what to eat to make up your daily calories and macros can help you build muscle faster. Here’s what to focus on.
- Best High-Protein Foods:
- Poultry
- Red Meat
- Fish
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- Cottage cheese
- Tofu
- Tempeh
- Quinoa
- Edamame
- Lentils
- Legumes
- Protein Supplements
- Best Carbs for Bodybuilding:
- Rice
- Potatoes
- Pasta
- Bread
- Whole Grains
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Fruits
- Vegetables
Here’s where you can learn more about nutrition for athletes and pre and post-workout nutrition.
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast can you build muscle?
You can typically build muscle in six to ten weeks. (1)
How fast can a beginner gain muscle?
A beginner can start gaining muscle within four weeks. (1)
How can I get big muscles in two weeks?
Unless you’re a total beginner (and eating enough protein and carbs to fuel your training and growth), you’re not likely to pack on a substantial amount of muscle in just two weeks. But don’t lose hope.
One way to help yourself look bigger almost instantly is to do a high-volume workout right before you take those photos or go to that event you’re looking forward to. That will fill your muscles with blood and help them have a “pumped” appearance. You may also want to go through your wardrobe (or go thrifting!) for clothes that fit just right to emphasize the parts of your body you want to show off.
What are the most effective exercises for rapid muscle growth?
Big compound movements like the deadlift, back squat, bench press, and overhead press can help you gain muscle in multiple areas fast, but the way you structure your program also has an impact.
References
- Hody S, Croisier JL, Bury T, Rogister B, Leprince P. Eccentric Muscle Contractions: Risks and Benefits. Front Physiol. 2019 May 3;10:536.
- Schoenfeld BJ, Ogborn DI, Vigotsky AD, Franchi MV, Krieger JW. Hypertrophic Effects of Concentric vs. Eccentric Muscle Actions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Sep;31(9):2599-2608.
- Schoenfeld, Brad J. The Mechanisms of Muscle Hypertrophy and Their Application to Resistance Training. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 24(10):p 2857-2872, October 2010.
- Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897.
- Baz-Valle E, Balsalobre-Fernández C, Alix-Fages C, Santos-Concejero J. A Systematic Review of The Effects of Different Resistance Training Volumes on Muscle Hypertrophy. J Hum Kinet. 2022 Feb 10;81:199-210.
- Schoenfeld BJ, Ogborn D, Krieger JW. Dose-response relationship between weekly resistance training volume and increases in muscle mass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2017 Jun;35(11):1073-1082.
- Enes A, DE Souza EO, Souza-Junior TP. Effects of Different Weekly Set Progressions on Muscular Adaptations in Trained Males: Is There a Dose-Response Effect? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2024 Mar 1;56(3):553-563.
- Aragon, Alan A. MS1; Schoenfeld, Brad J. PhD, CSCS, CSPS, FNSCA2. Magnitude and Composition of the Energy Surplus for Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: Implications for Bodybuilding and Physique Athletes. Strength and Conditioning Journal 42(5):p 79-86, October 2020.
- Devries, M. C., & Phillips, S. M. (2015). Supplemental Protein in Support of Muscle Mass and Health: Advantage Whey. Journal of Food Science, 80(S1), A8-A15.
- Kerksick CM, Arent S, Schoenfeld BJ, Stout JR, Campbell B, Wilborn CD, Taylor L, Kalman D, Smith-Ryan AE, Kreider RB, Willoughby D, Arciero PJ, VanDusseldorp TA, Ormsbee MJ, Wildman R, Greenwood M, Ziegenfuss TN, Aragon AA, Antonio J. International society of sports nutrition position stand: nutrient timing. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017 Aug 29;14:33.
- Buford TW, Kreider RB, Stout JR, Greenwood M, Campbell B, Spano M, Ziegenfuss T, Lopez H, Landis J, Antonio J. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2007 Aug 30;4:6.
- Biolo G, Maggi SP, Williams BD, Tipton KD, Wolfe RR. Increased rates of muscle protein turnover and amino acid transport after resistance exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 1995 Mar;268(3 Pt 1):E514-20.
- MacDougall JD, Gibala MJ, Tarnopolsky MA, MacDonald JR, Interisano SA, Yarasheski KE. The time course for elevated muscle protein synthesis following heavy resistance exercise. Can J Appl Physiol. 1995 Dec;20(4):480-6.
- Van Cauter E, Plat L. Physiology of growth hormone secretion during sleep. J Pediatr. 1996 May;128(5 Pt 2):S32-7.
[ad_2]
Source link

